What effects on food and nutrients while use microwave?
What are the benefits of a microwave oven?
Microwave ovens are generally used for time efficiency at most of all commercial applications, such as restaurants, in the office and at home. Although some of modern recipes has used microwave, but some of the traditional recipes are still using oven and stoves. Professional chefs generally find microwave ovens to be of limited usefulness because of browning,caramelization, and other flavour-enhancing reactions cannot occur due to the temperature range. On the other hand, people who want fast cooking times can use microwave ovens to prepare food or to reheat stored food (including commercially available pre-cooked frozen dishes) in only a few minutes. Microwave Ovens can also be used to defrost items that will later be cooked by traditional methods, cutting the time it takes to defrost foods naturally. Microwave ovens are also useful for the ease in which they can perform some traditionally cumbersome kitchen tasks, such as softening butter or melting chocolate. Popcorn is an item popular with microwave oven users.
What are the components of a microwave oven?
- High voltage power source, commonly a simple transformer or an electronic power converter, which passes energy to the magnetron
- Stirrer, which converts high-voltage electric energy to microwave radiation
- Magnetron control circuit (usually with a microcontroller)
- Waveguide (to control the direction of the microwaves)
- Turntable
- Cooking cavity
how does it work?




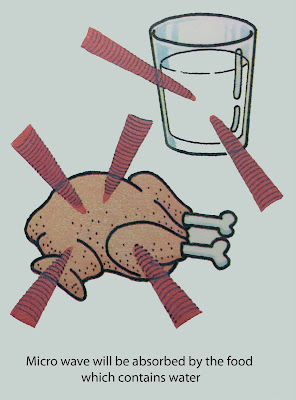




.jpg)